
 Emergency No: 08062136598
Emergency No: 08062136598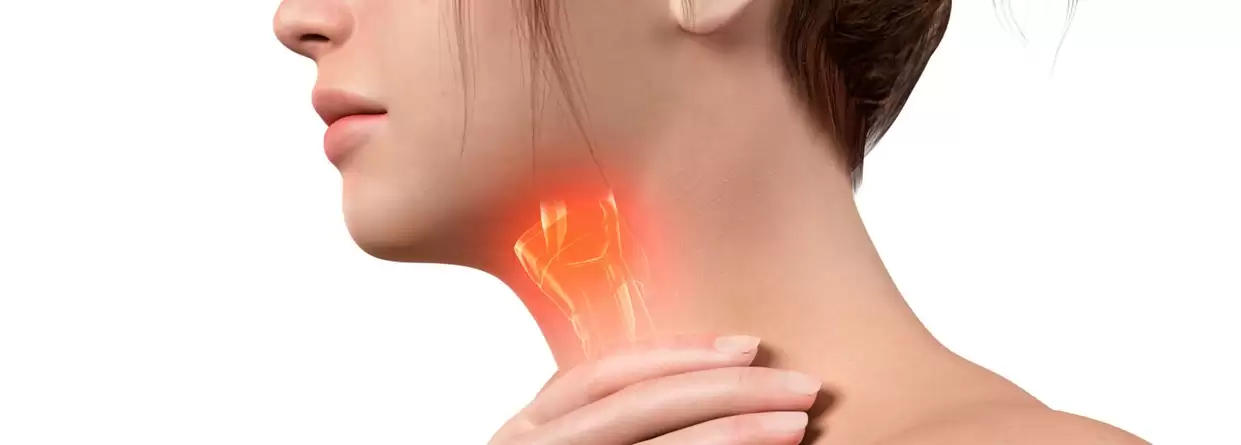
by CMRI | Published on 02/08/2020
Laryngeal cancer is a type of throat cancer that occurs in the tissue of the larynx or voice box. The larynx is about two inches wide and contains – vocal cords, muscles, and cartilages that help you to talk. Laryngeal cancer can develop in any part of the larynx but it mostly starts in the squamous cells or flat cells lining the inside of the larynx.
Besides, laryngeal cancer can permanently damage your voice. If not treated quickly, the cancer can spread to other parts of the body; from the back of the tongue, sections of throat and neck, to the lungs.
The symptoms of laryngeal cancer are relatively easy to detect. Some of the most common signs and symptoms include:
These signs and symptoms can also occur with other conditions. Nonetheless, to make sure, you should see the doctor if these symptoms last over a week.
Throat cancer is caused by damaged cells that start to overgrow and become tumors. In laryngeal cancer, such tumors normally originate in the larynx or voice box. But various risk factors – anything that increases the chance of developing a disease – can mutate these damaged cells.
For laryngeal cancer, common risk factors include excess smoking and heavy alcohol consumption. Those who smoke and consume one or more alcoholic drinks every day are more likely to develop laryngeal cancer. Prolonged exposure to second-hand smoke is also a major risk factor.
Besides, exposure to high levels of dangerous fumes and chemical substances for longer periods can also increase cancer risk. Harmful substances such as:
To diagnose laryngeal cancer, doctors start with your medical history and then, a series of tests are performed. The tests vary based on the symptoms shown. However, the first test is usually a laryngoscopy.
In a laryngoscopy, a laryngoscope – a thin tube with a camera and light at the end – is used to examine your mouth and throat, particularly your larynx. If your doctor finds any abnormalities, he may perform a biopsy in which a small tissue sample is examined under a microscope to test for cancer. Doctors usually rely on biopsy results to make the final diagnosis.
Moreover, doctors also use imaging tests to diagnose laryngeal cancer. They use an MRI or CT scan of the neck and head to assess the size of the tumor. These tests also help in determining if cancer has spread to lymph nodes in the neck.
In case your test reports come out positive, the doctor will order additional tests to determine the spread of the cancer. Nonetheless, an early diagnosis of laryngeal cancer can help support a successful treatment.
Treatment for laryngeal cancer will depend on the stage of the cancer. But like most cancers, laryngeal cancer is also treated with surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. Moreover, survival rates will depend on the location of cancer and how early it is diagnosed. However, survival rates usually decrease if cancer has metastasized or reached your lymph nodes.
In the early stages, doctors treat laryngeal cancer with surgery or radiation therapy. Cancer surgery includes the removal of the cancerous tumor and nearby tissue. However, cancer surgery involves certain risks. You may experience:
After the surgery, radiation therapy is used to kill the remaining cancer cells and shrink tumors. Or your doctor can only use radiation therapy to treat laryngeal cancer, provided it is small.
Another common cancer treatment is chemotherapy which uses a combination of drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy also amplifies the effects of radiation therapy. Your doctor may use pills or an infusion to medicate you.
The chemotherapy will enter your bloodstream and kill rapidly increasing cancerous cells and even healthy cells. Chemotherapy is also used to treat symptoms of advanced cancer that cannot be fully removed with surgery.
Furthermore, a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy is used to treat the advanced stages of laryngeal cancer.
The easiest way to prevent cancer of the larynx is to quit smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Also, by eliminating the consumption of tobacco in any form. Follow a healthy diet, including food rich in anti-oxidants to keep the cancer risk at bay.
You can significantly reduce the risk of laryngeal cancer with these lifestyle changes. As the adage goes, “prevention is better than cure”.